Canine FGF14 / SCA27 Protein
FGF14
- 100ug (NPP1274) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P70046-DNAE |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Canine |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | FGF14 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant canine FGF14 comprises 190 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 21.1 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 21 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 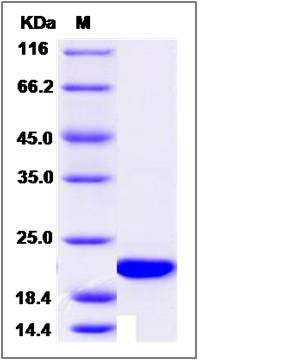 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the canine FGF14 (XP_003363267.1)(Lys64-Thr252)was expressed with a N-terminal Met. |
| Bio-activity | Immobilized canine FGF14 at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind human FGFR4-Fc (P10538-H02H) with a linear range of 0.16-2.5 μg/ml. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Cytokines & Growth Factors |Growth Factor & Receptor |Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) & Receptor |Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | FGF14 is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family. Members of this family possess broad mitogenic and cell survival activities, and are involved in a variety of biological processes, including embryonic development, cell growth, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth and invasion. FGF14 is probably involved in nervous system development and function. Defects in FGF14 are the cause of spinocerebellar ataxia type 27 (SCA27). It is a clinically and genetically heterogeneous group of cerebellar disorders. Patients show progressive incoordination of gait and often poor coordination of hands, speech and eye movements, due to degeneration of the cerebellum with variable involvement of the brainstem and spinal cord. SCA27 is an autosomal dominant cerebellar ataxia. It is a slowly progressive disorder, with onset in late-childhood to early adulthood, characterized by ataxia with tremor, orofacial dyskinesia, psychiatric symptoms and cognitive deficits. |
| Reference |
