Canine IL-8 / CXCL8 Protein
IL8, CXCL8
- 100ug (NPP3155) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P70009-DNAE |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Canine |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | IL8, CXCL8 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant canine IL8 comprises 80 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 9.2 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 9 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Ala 23 |
| SDS-PAGE | 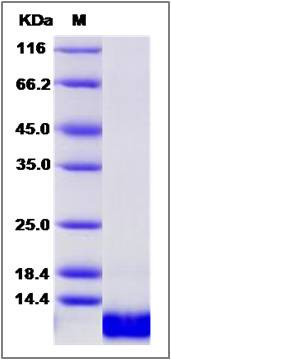 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the canine IL8 (P41324) (Ala23-Pro101) was expressed, with a N-terminal Met. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cardiovascular |Angiogenesis |Cytokine & Receptor |Interleukin & Receptor |Other Interleukin & Receptor |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS 0.5mM TCEP pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Interleukin 8 (IL-8), also known as CXCL8, which is a chemokine with a defining CXC amino acid motif that was initially characterized for its leukocyte chemotactic activity, is now known to possess tumorigenic and proangiogenic properties as well. This chemokine is secreted by a variety of cell types including monocyte/macrophages, T cells, neutrophils, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and various tumor cell lines in response to inflammatory stimuli (IL1, TNF, LPS, etc). In human gliomas, IL-8 is expressed and secreted at high levels both in vitro and in vivo, and recent experiments suggest it is critical to glial tumor neovascularity and progression. Levels of IL-8 correlate with histologic grade in glial neoplasms, and the most malignant form, glioblastoma, shows the highest expression in pseudopalisading cells around necrosis, suggesting that hypoxia/anoxia may stimulate expression. Interleukin (IL)-8/CXCL8 is a potent neutrophil chemotactic factor. Accumulating evidence has demonstrated that various types of cells can produce a large amount of IL-8/CXCL8 in response to a wide variety of stimuli, including proinflammatory cytokines, microbes and their products, and environmental changes such as hypoxia, reperfusion, and hyperoxia. Numerous observations have established IL-8/CXCL8 as a key mediator in neutrophil-mediated acute inflammation due to its potent actions on neutrophils. However, several lines of evidence indicate that IL-8/CXCL8 has a wide range of actions on various types of cells, including lymphocytes, monocytes, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts, besides neutrophils. The discovery of these biological functions suggests that IL-8/CXCL8 has crucial roles in various pathological conditions such as chronic inflammation and cancer. IL-8 has been associated with tumor angiogenesis, metastasis, and poor prognosis in breast cancer. IL-8 may present a novel therapeutic target for estrogen driven breast carcinogenesis and tumor progression. |
| Reference |
