Canine PD-L1 / B7-H1 / CD274 Protein (Fc Tag)
PD-L1, B7-H1, CD274
- 100ug (NPP1566) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P70110-D02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Canine |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | PD-L1, B7-H1, CD274 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant canine CD274 consists 456 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 51.5 kDa. |
| predicted N | Phe 19 |
| SDS-PAGE | 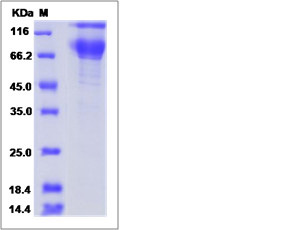 |
| Purity | > (17.0+77.6) % as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the canine CD274 (XP_541302.4) (Met1-Arg236) was expressed with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Innate Immunity |Monocytes/Macrophages |Macrophage Markers |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Programmed death-1 ligand-1 (PD-L1, CD274, B7-H1) has been identified as the ligand for the immunoinhibitory receptor programmed death-1(PD1/PDCD1) and has been demonstrated to play a role in the regulation of immune responses and peripheral tolerance. PD-L1/B7-H1 is a member of the growing B7 family of immune molecules and this protein contains one V-like and one C-like Ig domain within the extracellular domain, and together with PD-L2, are two ligands for PD1 which belongs to the CD28/CTLA4 family expressed on activated lymphoid cells. By binding to PD1 on activated T-cells and B-cells, PD-L1 may inhibit ongoing T-cell responses by inducing apoptosis and arresting cell-cycle progression. Accordingly, it leads to growth of immunogenic tumor growth by increasing apoptosis of antigen specific T cells and may contribute to immune evasion by cancers. PD-L1 thus is regarded as promising therapeutic target for human autoimmune disease and malignant cancers. |
| Reference |
