Canine RBP4 Protein (Fc Tag)
RBP4
- 100ug (NPP1834) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P70006-D02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Canine |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | RBP4 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant canine RBP4 comprises 424 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 48 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 53 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Glu 19 |
| SDS-PAGE | 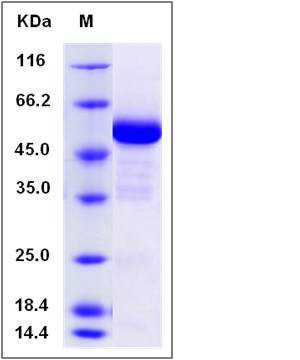 |
| Purity | > 94 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the canine RBP4 (F1PQI4) (Met1-Leu201) was expressed, fused with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to bind alltrans retinoic acid. The binding of retinoic acid results in the quenching of Trp fluorescence in RBP4. The 50% binding concentration (BC50) is >5 µM |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Metabolism |Types of disease |Metabolism in Heart disease |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Retinol-binding protein 4 (RBP4) is the specific carrier for retinol (also known as vitamin A), and is responsible for the conversion of unstable and insoluble retinol in aqueous solution into stable and soluble complex in plasma through their tight interaction. As a member of the lipocalin superfamily, RBP4 containing a β-barrel structure with a well-defined cavity is secreted from the liver, and in turn delivers retinol from the liver stores to the peripheral tissues. In plasma, the RBP4-retinol complex interacts with transthyretin (TTR), and this binding is crucial for preventing RBP4 excretion through the kidney glomeruli. RBP4 expressed from an ectopic source efficiently delivers retinol to the eyes, and its deficiency affects night vision largely. Recently, RBP4 as an adipokine, is found to be expressed in adipose tissue and correlated with obesity, insulin resistance (IR) and type 2 diabetes (T2DM). |
| Reference |
