Cynomolgus ALK-2 / ACVR1 / ALK2 Protein (Fc Tag)
ACVR1
- 100ug (NPP4404) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P90058-C02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Cynomolgus |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | ACVR1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant cynomolgus ACVR1 is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 342 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 38.2 KDa.The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 44 and 37 KDa respectively in SDS-PAGE. |
| predicted N | Asp 23 |
| SDS-PAGE | 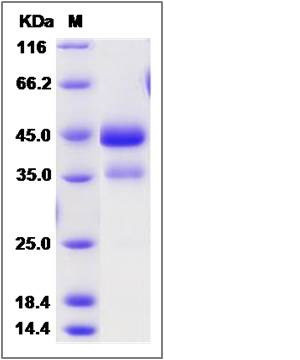 |
| Purity | (75.3+22.3) % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the cynomolgus ACVR1 (F7A9J8) (Met1-Glu123) was expressed with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Invasion microenvironment |Angiogenesis |Growth Factor & Receptor |Transforming Growth Factor Beta (TGF-beta) Superfamily |Transforming Growth Factor Beta (TGF-beta) Family | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | ALK-2, also termed as ACVR1, was initially identified as an activin type I receptor because of its ability to bind activin in concert with ActRII or ActRIIB. ALK-2 is also identified as a BMP type I receptor. It has been demonstrated that ALK-2 forms complex with either the BMP-2/7-bound BMPR-II or ACVR2A /ACVR2B. ALK-1 and ALK-2 presenting in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae are two haspin homologues. Both ALK-1 and ALK-2 exhibit a weak auto-kinase activity in vitro, and are phosphoproteins in vivo. ALK-1 and ALK-2 levels peak in mitosis and late-S/G2. Control of protein stability plays a major role in ALK-2 regulation. The half-life of ALK-2 is particularly short in G1. Overexpression of ALK-2, but not of ALK-1, causes a mitotic arrest, which is correlated to the kinase activity of the protein. This suggests a role for ALK-2 in the control of mitosis. Endoglin is phosphorylated on cytosolic domain threonine residues by the TGF-beta type I receptors ALK-2 and ALK-5 in prostate cancer cells. Endoglin did not inhibit cell migration in the presence of constitutively active ALK-2. Defects in ALK-2 are a cause of fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP). |
| Reference |
