Cynomolgus CD200Rla Protein (Fc Tag)
CD200RLa
- 100ug (NPP4408) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11576-C02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Cynomolgus |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CD200RLa |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant cynomolgus CD200RLa/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer consists of 460 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 51.3 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the CD200RLa/Fc monomer is approximately 70-85 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Met 22 |
| SDS-PAGE | 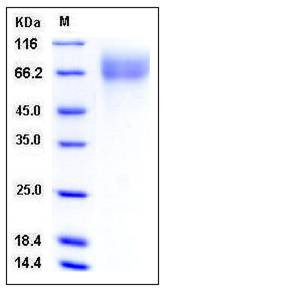 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the Cynomolgus (Macaca fascicularis) CD200RLa extracellular domain (Met 1-Leu 240) was as fused with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Epigenetics |Transcription |Co-factors |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Cell surface glycoprotein CD200 receptor 2, also known as Cell surface glycoprotein CD200 receptor 1-like, Cell surface glycoprotein OX2 receptor 2, CD200 receptor-like 2, CD200Rla, CD200R1L and CD200R2, is a single-pass type I membrane protein which belongs to the CD200R family. CD200R1L / CD200R2. It contains one Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domain and one Ig-like V-type (immunoglobulin-like) domain. CD200 is a transmembrane protein delivering immunoregulatory signals after engagement of CD200R. A family of CD200Rs exist ( CD200R1, CD200R2, CD200R3, CD200R4 ) with different tissue expression and functional activity. In the presence of anti-CD200R2 / CD200R3 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), bone-marrow cells cultured in the presence of (interleukin [IL]-4+granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor) differentiate into dendritic cells (DCs), which induce CD4+CD25+ Treg. Interaction between the relatively ubiquitously expressed molecule CD200 and one of its receptors, CD200R1, resulted in direct suppression of alloreactivity, engagement of alternate receptors led instead to altered differentiation of dendritic cells (DCs) from marrow precursors, which could in turn foster development of Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells. Unlike anti-CD200R1, anti-CD200R2 both promotes development of DCs with capacity to induce Treg and directly augments thymocyte production of Treg. |
| Reference |
