Cynomolgus CD3d / CD3 delta Protein (Fc Tag)
CD3D
- 100ug (NPP4411) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P90046-C02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Cynomolgus |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CD3D |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human cynomolgus /Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 325 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 36.6 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 44-49 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Phe 22 |
| SDS-PAGE | 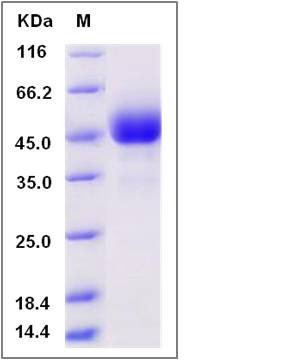 |
| Purity | > 99 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the cynomolgus CD3D (Q95LI8) (Met1-Ala105) was expressed, fused with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Cluster of Differentiation (CD) |B Cell CD Antigen |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | T-cell surface glycoprotein CD3 delta chain, also known as CD3D, is a single-pass type I membrane protein. CD3D, together with CD3-gamma, CD3-epsilon and CD3-zeta, and the T-cell receptor alpha/beta and gamma/delta heterodimers, forms the T cell receptor-CD3 complex. The majority of T cell receptor (TCR) complexes in mice and humans consist of a heterodimer of polymorphic TCRalpha and beta chains along with invariant CD3gamma, delta, epsilon, and zeta chains. CD3 chains are present as CD3gammaepsilon, deltaepsilon, and zetazeta dimers in the receptor complex and play critical roles in the antigen receptor assembly, transport to the cell surface, and the receptor-mediated signal transduction. T cell receptor-CD3 complex plays an important role in coupling antigen recognition to several intracellular signal-transduction pathways. This complex is critical for T-cell development and function, and represents one of the most complex transmembrane receptors. The T cell receptor-CD3 complex is unique in having ten cytoplasmic immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs). CD3D contains 1 ITAM domain and has been shown to interact with CD8A. In the mouse, knockout of CD3delta allows some degree of T lymphocyte differentiation since mature CD4 and CD8 as well as TCRgammadelta T lymphocytes are observed in the periphery. In contrast, deleterious mutation of the CD3delta encoding gene in the human leads to a severe combined immunodeficiency characterised by the complete absence of mature T cell subpopulations including TCRalpha/beta and TCRgamma/delta. Defects in CD3D cause severe combined immunodeficiency autosomal recessive T-cell-negative/B-cell-positive/NK-cell-positive (T-/B+/NK+ SCID) which is a genetically and clinically heterogeneous group of rare congenital disorders characterized by impairment of both humoral and cell-mediated immunity, leukopenia, and low or absent antibody levels. In humans the absence of CD3 delta results in a complete arrest in thymocyte development at the stage of double negative to double positive transition and the development of gamma delta T-cell receptor-positive T cells is also impaired. |
| Reference |
