Cynomolgus CD53 Protein (aa 107-181, Fc Tag)
CD53
- 100ug (NPP1840) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P90189-C04H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Cynomolgus |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CD53 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant cynomolgus CD53 is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 311 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 34.9 KDa. The apparent molecular mass of it is approximately 44 KDa respectively in SDS-PAGE. |
| predicted N | Asp |
| SDS-PAGE | 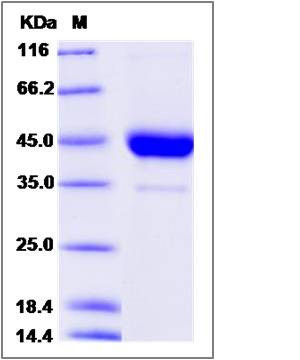 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the cynomolgus CD53 (G7NW46) (Glu107-Asn181) was expressed with the Fc region of mouse IgG1 at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Adapters |Transmembrane |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, PH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | CD53 is a member of the transmembrane 4 superfamily, also called the tetraspanin family. Most of these members are cell-surface proteins that are characterized by the presence of four hydrophobic domains. These proteins mediate signal transduction events that play a role in the regulation of cell development, activation, growth and motility. CD53 is a cell surface glycoprotein that is known to complex with integrins. Familial deficiency of CD53 gene has been linked to an immunodeficiency associated with recurrent infectious diseases caused by bacteria, fungi and viruses. CD53 contributes to the transduction of CD2-generated signals in T cells and natural killer cells and has been suggested to play a role in growth regulation. |
| Reference |
