Cynomolgus CD59 / CD59A / MAC-IP Protein (His Tag)
CD59
- 100ug (NPP4412) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P90188-C08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Cynomolgus |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CD59 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant cynomolgus CD59 comprises 87 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 10.2 KDa. The apparent molecular mass of it is approximately 18 and 14 KDa respectively in SDS-PAGE. |
| predicted N | Leu 26 |
| SDS-PAGE | 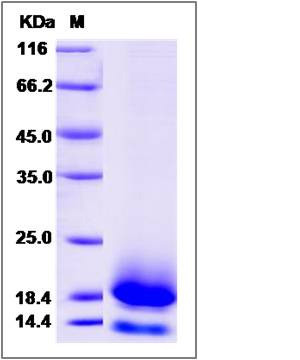 |
| Purity | (77.8+20.8) % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the cynomolgus CD59 (G7PQF7) (Met1-Glu101) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cardiovascular |Atherosclerosis |Vascular Inflammation |Innate and adaptive immunity |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, PH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | CD59 glycoprotein, also known as 20 kDa homologous restriction factor, HRF20, MAC-inhibitory protein, Membrane attack complex inhibition factor, Membrane inhibitor of reactive lysis, MIC11, MIRL and CD59, is a cell membrane protein which contains one UPAR/Ly6 domain. CD59 is a small, highly glycosylated, GPI-linked protein, with a wide expression profile. The soluble form of CD59 from urine retains its specific complement binding activity, but exhibits greatly reduced ability to inhibit MAC assembly on cell membranes. CD59 is a potent inhibitor of the complement membrane attack complex (MAC) action. CD59 was first identified as a regulator of the terminal pathway of complement. It acts by binding to the C8 and/or C9 complements of the assembling MAC, thereby preventing incorporation of the multiple copies of C9 required for complete formation of the osmolytic pore. This inhibitor appears to be species-specific. CD59 is involved in signal transduction for T-cell activation complexed to a protein tyrosine kinase. Defects in CD59 are the cause of CD59 deficiency (CD59D). |
| Reference |
