Cynomolgus CD62L / L-Selectin / SELL Protein (His Tag)
SELL
- 100ug (NPP4445) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P90168-C08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Cynomolgus |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | SELL |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant cynomolgus SELL comprises 315 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 35.6 KDa. The apparent molecular mass of it is approximately 52-63 KDa respectively in SDS-PAGE. |
| predicted N | Asp 29 |
| SDS-PAGE | 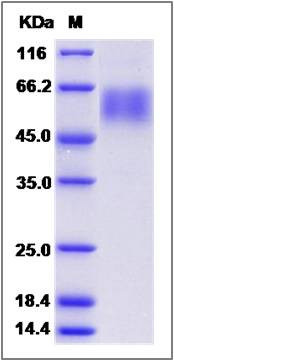 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the cynomolgus SELL (Met1-Asn332) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by the ability of the immobilized protein to support the adhesion of U937 human histiocytic lymphoma cells. When 5 x 10E4 cells/well are added to cyno L-Selectin coated plates (10 μg/mL, 100 μL/well), > 60% cells will adhere after 1 hour at 37℃. |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Cytoskeleton / ECM |Cell Adhesion |Lectin |C-tyep lectin | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | L-selectin (SELL), also known as CD62L, is a key adhesion molecule that regulates both the migration of leukocytes at sites of inflammation and the recirculation of lymphocytes between blood and lymphoid tissues. It belongs to the selectin family of proteins, and consisting of a large, highly glycosylated, extracellular domain, a single spanning transmembrane domain and a small cytoplasmic tail. L-selectin is the only selectin expressed on leukocytes and mediates a number of leukocyte-endothelial interactions. L-selectin acts as a "homing receptor" for leukocytes to enter secondary lymphoid tissues via high endothelial venules. Ligands present on endothelial cells will bind to leukocyte expressing L-selectin, slowing leukocyte trafficking through the blood, and facilitating entry into a secondary lymphoid organ at that point. L-selectin-mediated lymphocyte recirculation is required for maintaining the appropriate tissue distribution of lymphocyte subpopulations including naïve and effector subsets such as regulatory T cells. In addition, L-selectin-mediated entry into peripheral lymph nodes is required for optimal induction of lymphocyte homeostatic proliferation during lymphopenia. Importantly, L-selectin has been shown to have both adhesive and signaling functions during leukocyte migration. L-selectin has also been shown to mediate leukocyte recruitment during chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases and thus is a potential therapeutic target for drug development. |
| Reference |
