Cynomolgus CD80 / B7-1 Protein (His Tag)
CD80, B7-1
- 100ug (NPP1178) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P90268-C08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Cynomolgus |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CD80, B7-1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant cynomolgus CD80 consists 219 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 25.4 kDa. |
| predicted N | Val 35 |
| SDS-PAGE | 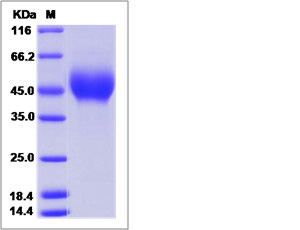 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the cynomolgus CD80 (Met1-Asn242) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Embryogenesis |Germ Layer Formation |Ectoderm Marker |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | The B-lymphocyte activation antigen B7-1 (referred to as B7), also known as CD80, is a member of cell surface immunoglobulin superfamily and is expressed on the surface of antigen-presenting cells including activated B cells, macrophages and dendritic cells. As costimulatory ligands, B7-1 which exists predominantly as dimer and the related protein B7-2, interact with the costimulatory receptors CD28 and cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) expressed on T cells, and thus constitute one of the dominant pathways that regulate T cell activation and tolerance, cytokine production, and the generation of CTL. The B7/CD28/CTLA4 pathway has the ability to both positively and negatively regulate immune responses. CD80 is thus regarded as promising therapeutic targets for autoimmune diseases and various carcinomas. |
| Reference |
