Cynomolgus FAS / CD95 / APO-1 / TNFRSF6 Protein (Fc Tag)
FAS
- 100ug (NPP4428) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P90273-C02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Cynomolgus |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | FAS |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant cynomolgus FAS is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 389 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 43.8 KDa.The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 47-57 KDa in SDS-PAGE. |
| predicted N | Gln 26 |
| SDS-PAGE | 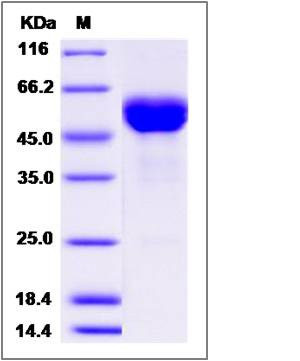 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the cynomolgus FAS (F6V1W6) (Met1-Asp173) was expressed with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | 1. Measured by its ability to inhibit Fas Ligand induced apoptosis of Jurkat human acute T cell leukemia cells. The ED50 for this effect is typically 0.2-0.8 μg/mL in the presence of 20 ng/mL recombinant human Fas ligand. 2. Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized human His-FASLG (Cat:10244-H07Y) at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind Cynomolgus FAS-Fc. The EC50 of Cynomolgus FAS-Fc is 0.06-0.14 μg/ml. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Other Related Intracellular Topics |Regulation of Apoptosis by TNF Superfamily Members |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | CD95 (APO-1/Fas) is an important inducer of the extrinsic apoptosis signaling pathway and therapy induced apoptosis of many tumor cells has been linked to the activity of CD95. is a prototype death receptor characterized by the presence of an 80 amino acid death domain in its cytoplasmic tail. This domain is essential for the recruitment of a number of signaling components upon activation by either agonistic anti-CD95 antibodies or cognate CD95 ligand that initiate apoptosis. The complex of proteins that forms upon triggering of CD95 is called the death-inducting signaling complex (DISC). The DISC consists of an adaptor protein and initiator caspases and is essential for induction of apoptosis. CD95 is also crucial for the negative selection of B cells within the germinal center (GC). Impairment of CD95-mediated apoptosis results in defective affinity maturation and the persistence of autoreactive B-cell clones. Changes in the expression of CD95 and/or its ligand CD95L are frequently found in human cancer. The downregulation or mutation of CD95 has been proposed as a mechanism by which cancer cells avoid destruction by the immune system through reduced apoptosis sensitivity. Thus, CD95 has therefore been viewed as a tumor suppressor. CD95 has been reported to be involved in the activation of NF-kappaB, MAPK3/ERK1, MAPK8/JNK, and the alternate pathways for CTL-mediated cytotoxicity. Accordingly, this protein is implicated in the pathogenesis of various malignancies and diseases of the immune system. The CD95/CD95L system was implicated in the etiology of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) based, primarily, on the finding that CD95 is highly expressed in the intestinal epithelial cells and that epithelial apoptosis is increased in IBD. |
| Reference |
