Cynomolgus / Human TNFSF12 Protein (Fc Tag)
TNFSF12
- 100ug (NPP1718) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P90094-C04H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Cynomolgus |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | TNFSF12 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant cynomolgus TNFSF12 is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 392 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 43.8 KDa. The apparent molecular mass of it is approximately 34 and 47 KDa respectively in SDS-PAGE. |
| predicted N | Asp |
| SDS-PAGE | 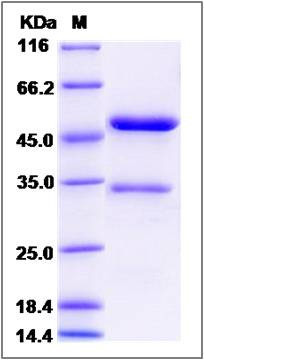 |
| Purity | (72.2+25.9) % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the cynomolgus TNFSF12 (F7HGN4) (Ser94-His249) was expressed with the Fc region of mouse IgG1 at the N-terminus. Cynomolgus and Human TNFSF12 sequences are identical. |
| Bio-activity | 1. Measured in a cell proliferation assay using HUVEC human umbilical vein endothelial cells. The ED50 for this effect is typically 2-8 ng/mL. 2. Immobilized Cynomolgus mFc-TNFSF12 at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind human Fc-TNFRSF12A (P10431-H01H), The EC50 of human Fc-TNFRSF12A (P10431-H01H) is 0.07-0.15 μg/ml. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Other Related Intracellular Topics |Regulation of Apoptosis by TNF Superfamily Members |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | TNFSF12 is a cytokine that belongs to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) ligand family. It is a ligand for the FN14/TWEAKR receptor. TNFSF12 has overlapping signaling functions with TNF, but displays a much wider tissue distribution. It can induce apoptosis via multiple pathways of cell death in a cell type-specific manner. It is also found that TNFSF12 promotes proliferation and migration of endothelial cells, and thus acts as a regulator of angiogenesis. TNFSF12 also is a weak inducer of apoptosis in some cell types and mediates NF-kappa-B activation. |
| Reference |
