Cynomolgus Neuropilin-1 / NRP1 Protein
NRP1
- 100ug (NPP4419) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P90297-CCCH |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Cynomolgus |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | NRP1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant cynomolgus NRP1 is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 599 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 67.5 KDa.The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 67-77 KDa in SDS-PAGE. |
| predicted N | Ala 25 |
| SDS-PAGE | 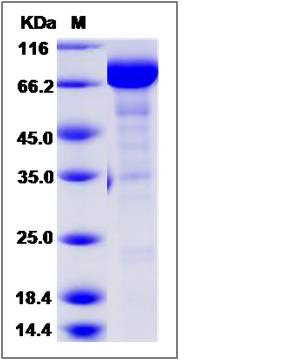 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the cynomolgus NRP1 (G7PEQ1) (Met1-Gly613) was expressed with six amino acids (LEVLFQ) at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Oncoprotein & suppressor & biomarker |Oncoprotein |Growth Factor & Receptor |Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) & Receptor |VEGF Receptor | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Neuropilin is a type I transmembrane protein and the molecular mass is 120 kDa. Two homologues, Neuropilin-1 and Neuropilin-2, are identified. The primary structure of Neuropilin-1 and Neuropilin-2 is well conserved and is divided into four domains, CUB (a1/a2) domain, FV/FVIII (b1/b2) domain, MAM (c) domain, and (d) domain that contains a transmembrane and a short cytoplasmic region. Neuropilin-1 (NRP1) acts as a receptor for two different extracellular ligands, class 3 semaphorins and specific isoforms of vascular endothelial growth factor. The functions of NRP1 and NRP2 have been extensively studied in neurons where they act in axon guidance and in endothelial cells where they promote angiogenesis and cell migration. Neuropilin-1 is likely to mediate contacts between the dendritic cells and the T lymphocytes via homotypic interactions and is essential for the initiation of the primary immune response. NRP1 is a co-receptor for VEGF receptor-2 (VEGFR2) that enhances the binding of VEGF165 to VEGFR2 and VEGF165-mediated chemotaxis. NRP1 expression is regulated in EC by tumor necrosis factor-alpha, the transcription factors dHAND and Ets-1, and vascular injury. NRP1 upregulation is positively correlated with the progression of various tumors. Overexpression of NRPI in rat tumor cells results in enlarged tumors and substantially enhanced tumor angiogenesis. On the other hand, soluble NRP1 (sNRP1) is an antagonist of tumor angiogenesis. |
| Reference |
