Cynomolgus PDGF-C / PDGFC Protein (Fc Tag)
PDGF-C, PDGFC
- 100ug (NPP4440) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P90031-C01H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Cynomolgus |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | PDGF-C, PDGFC |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant cynomolgus PDGFC comprises 371 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 40.9 KDa. |
| predicted N | Glu |
| SDS-PAGE | 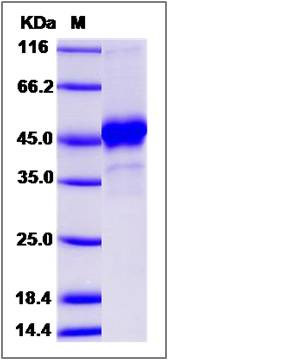 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the cynomolgus PDGFC (EHH54037.1) (Val235-Gly345) was expressed with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured in a cell proliferation assay using Balb/c 3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblasts. The ED50 for this effect is typically 60-300 ng/ml. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Invasion microenvironment |Angiogenesis |Growth Factor & Receptor |Platelet-Derived Growth Factor (PDGF) & Receptor |Platelet-Derived Growth Factor (PDGF) | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | PDGF-C is a member of the PDGF/VEGF family of growth factors with a unique domain organization and expression pattern. Platelet-derived growth factor receptors (PDGFRs) are catalytic receptors that have intracellular tyrosine kinase activity. They have roles in the regulation of many biological processes including embryonic development, angiogenesis, cell proliferation and differentiation, and contribute to the pathophysiology of some diseases, including cancer. There are two isoforms of the PDGFR receptor; PDGFRalpha and PDGFRbeta, which can form homo- or heterodimers. The endogenous PDGFR ligands are PDGF-A, -B, -C and -D, which induce receptor dimerization and transphosphorylation at specific tyrosine residues upon binding. This activates the intracellular kinase activity, initiating intracellular signaling through the MAPK, PI 3-K and PKCgamma pathways. PDGF-C acts as a specific ligand for alpha platelet-derived growth factor receptor homodimer, and alpha and beta heterodimer. Binding of this growth factor to its affinity receptor elicits a variety of cellular responses. PDGF-C Appears to be involved in the three stages of wound healing: inflammation, proliferation and remodeling. Involved in fibrotic processes, in which transformation of interstitial fibroblasts into myofibroblasts plus collagen deposition occurs. |
| Reference |
