Cynomolgus / Rhesus Angiopoietin-2 / ANG2 Protein (His Tag)
Angiopoietin-2, ANG2
- 100ug (NPP4420) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P90026-C07H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Cynomolgus |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | Angiopoietin-2, ANG2 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant cynomolgus ANGPT2 consists 241 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 27.7 kDa. |
| predicted N | His |
| SDS-PAGE | 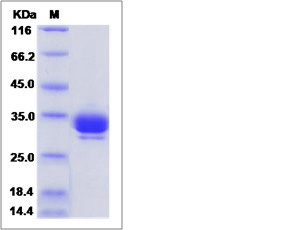 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the cynomolgus ANGPT2 (XP_005562585.1) (Lys274-Phe495) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the N-terminus. Cynomolgus and Rhesus ANGPT2 sequences are identical. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized Cynomolgus ANGPT2 at 10 μg/ml (100 μl /well) can bind Cynomolgus TEK-Fc (P90292-C02H ), The EC50 of Cynomolgus TEK-Fc (P90292-C02H ) is 20-60 ng/ml. |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Growth Factor & Receptor |Hormones |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Angiopoietin-2 (ANG 2, or ANGPT2), is a member of the ANG family, which plays an important role in angiogenesis during the development and growth of human cancers. Both ANGPT-1 and ANGPT-2 appear to bind to the tyrosine kinase receptor, Tie-2, found primarily on the luminal surface of endothelial cells. ANG-2's role in angiogenesis generally is considered as an antagonist for ANG1, inhibiting ANG1-promoted Tie2 signaling, which is critical for blood vessel maturation and stabilization. ANG-2 modulates angiogenesis in a cooperative manner with another important angiogenic factor, vascular endothelial growth factor A. Genetic studies have revealed that ANG-2 also is critical in lymphangiogenesis during development. ANG-2 has multiple physiologic effects that regulate vascular tone, hormone secretion, tissue growth and neural activity. Several reports indicate that ANG-2 can induce neovascularization in experimental systems due to the expression of different growth factors such as angiopoietin 2, vascular endothelial factor, and its receptor, fibroblast growth factor, platelet derived growth factor, transforming growth factor beta and epidermal growth factor. In addition, ANG-2 is strongly expressed in the vasculature of many tumors and it has been suggested that ANG-2 may act synergistically with other cytokines such as vascular endothelial growth factor to promote tumor-associated Angiogenesis and tumor progression. |
| Reference |
