Cynomolgus TNFR2 / CD120b / TNFRSF1B Protein (Fc Tag)
TNFRSF1B
- 100ug (NPP4450) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P90102-C02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Cynomolgus |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | TNFRSF1B |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant cynomolgus TNFRSF1B is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 476 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 52.1 KDa.The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 68 KDa respectively in SDS-PAGE. |
| predicted N | Leu 25 |
| SDS-PAGE | 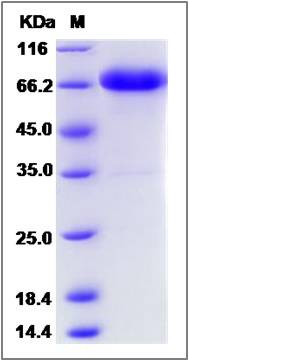 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the cynomolgus TNFRSF1B (F7EAE4) (Met1-Asp257) was expressed with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to inhibit the TNFα mediated cytotoxicity in the L-929 mouse fibroblast cells in the presence of the metabolic inhibitor actinomycin D. The ED50 for this effect is typically 2-10 ng/mL in the presence of 1 ng/mL of cynoTNFα. |
| Research Area | Cardiovascular |Atherosclerosis |Ischemia / Reperfusion |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 1B (TNFRSF1B), also known as Tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 (TNFR2) or CD120b antigen, is a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily. TNFR2/CD120b/TNFRSF1B is a member of the TNF-receptor superfamily. This protein and TNF-receptor 1 form a heterocomplex that mediates the recruitment of two anti-apoptotic proteins, c-IAP1 and c-IAP2, which possess E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. Knockout studies in mice also suggest a role of this protein in protecting neurons from apoptosis by stimulating antioxidative pathways. TNFR2/CD120b/TNFRSF1B is not a major contributing factor to the genetic risk of type 2 diabetes, its associated peripheral neuropathy and hypertension and related metabolic traits in North Indians. Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 1B (TNFRSF1B) has been reported to be associated with SLE risk in Japanese populations. TNFR2/CD120b/TNFRSF1B serves as a receptor with high affinity for TNFSF2 and approximately 5-fold lower affinity for homotrimeric TNFSF1. This receptor mediates most of the metabolic effects of TNF-alpha. Isoform 2 blocks TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis, which suggests that it regulates TNF-alpha function by antagonizing its biological activity. |
| Reference |
