Cynomolgus aFGF / FGF1 Protein
FGF1
- 100ug (NPP1048) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P90062-CNAE |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Cynomolgus |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | FGF1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant cyno FGF1 consists of 141 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 16 kDa. It migrates as an 16 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 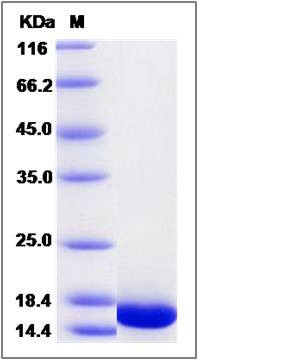 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the cyno FGF1 (Phe16-Asp155) was expressed and purified with an initial Met. |
| Bio-activity | Measured in a cell proliferation assay using BALB/c 3T3 mouse fibroblasts. The ED50 for this effect is typically 0.1-0.4 ng/mL. |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Growth Factor & Receptor |Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) & Receptor |Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4, 20% glycerol. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | aFGF, also known as FGF1 and HBGF-1, is a member of the fibroblast growth factor family. The biological activity of aFGF protein is exerted through binding to four high affinity cell surface receptors (FGFR1–4), which results in receptor dimerization and transphosphorylation in the tyrosine kinase domain. aFGF protein shows a wide range of endocrine-like activities. As a multiple function growth factor, this protein is involved in embryo development and tissue repair. Additionally, this protein is considered to function in several important physiological and pathological processes, such as embryonic development, morphogenesis, angiogenesis, wound healing and atheromatosis, carcinogenesis, development, and invasion of cancer. |
| Reference |
