HIV-1 gp120 Protein (group M, subtype CRF07_BC) (His Tag)
- 100ug (NPP2961) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11233-V08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | HIV |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant HIV-1 gp120 consists of 486 amino acids after removal of the signal peptide and has a predicted molecular mass of 54.6 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the recombinant protein is approximately 80-100 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Ala 29 |
| SDS-PAGE | 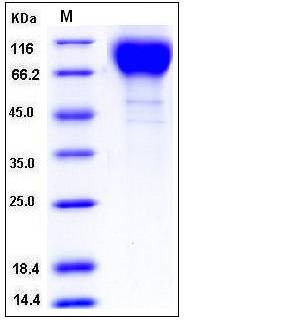 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein gp160 (AFM77980.1) extracellular domain (Ala 29-Glu 503), termed as gp120, was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Microbiology |Pathogenic microorganism |viruses |animal virus |viral illness |Immune system illness | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | The HIV-1 gp120 envelope protein, a glycoprotein that is part of the outer layer of the virus, which is an essential component in the multi-tiered viral entry process. It presents itself as viral membrane spikes consisting of 3 molecules of gp120 linked together and anchored to the membrane by gp41 protein. Gp120 is essential for viral infection as it facilitates HIV entry into the host cell and this is its best-known and most researched role in HIV infection. However, it is becoming increasingly evident that gp120 might also be facilitating viral persistence and continuing HIV infection by influencing the T cell immune response to the virus. The surface protein gp120 attaches the virus to the host lymphoid cell by binding to the primary receptor CD4. Gp120 binding to its receptor CD4 and co-receptor, CXCR4 or CCR5 is required for fusion of viral and cellular membranes. Several mechanisms might be involved in this process of which gp120 binding to the CD4 receptor of T cells is the best known and most important interaction as it facilitates viral entry into the CD4+ cells and their depletion, a hallmark of the HIV infection. Gp120 is shed from the viral membrane and accumulates in lymphoid tissues in significant amounts. Despite the overall genetic heterogeneity of the gp120 glycoprotein, the conserved CD4 binding site provides an attractive antiviral target. Interaction between gp120 and ITGA4/ITGB7 would allow the virus to enter GALT early in the infection, infecting and killing most of GALT's resting CD4+ T-cells. This T-cell depletion is believed to be the major insult to the host immune system leading to AIDS. |
| Reference |
