Human ABHD14B Protein (His Tag)
CIB,HEL-S-299
- 100ug (NPP1857) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P13913-H07E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | CIB,HEL-S-299 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human ABHD14B consists of 225 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 24.2 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 24 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | His |
| SDS-PAGE | 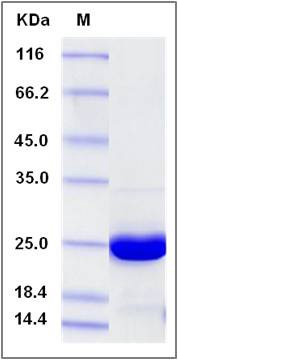 |
| Purity | > 96 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mature form of human ABHD14B (Q96IU4-1) (Met1-Gln210) was expressed with a polyhistide tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |G Protein-Coupled Receptors (GPCRs) |Chemokine Receptors |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, 20% glycerol, 50mM Arg, 0.1% Tween20, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | ABHD14B belongs to the AB hydrolase superfamily, ABHD14 family. It can be detected in spleen, thymus, prostate, testis, ovary, small intestine, colon, peripheral blood leukocyte, heart, placenta, lung, liver, skeletal muscle, pancreas and kidney. ABHD14B has hydrolase activity towards p-nitrophenyl butyrate (in vitro) and may interact with TAF1. It may activate transcription. Recombinant human ABHD14B protein, fused to His-tag at N-terminus, was expressed in E.coli and purified by using conventional chromatography techniques. ABHD14B contains an alpha/beta hydrolase fold, which is a catalytic domain found in a very wide range of enzymes. In molecular biology, the alpha/beta hydrolase fold is common to a number of hydrolytic enzymes of widely differing phylogenetic origin and catalytic function. The Ab hydrolase domain containing gene subfamily is comprised of 15 mostly uncharacterized members. |
| Reference |
