Human ACVR2B / ActivinR-IIB Protein (Fc Tag)
Activin RIIB,ActR-IIB,ACTRIIB,HTX4
- 100ug (NPP1046) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10229-H02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | Activin RIIB,ActR-IIB,ACTRIIB,HTX4 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human ACVR2B/Fc chimera is a disulfide-linked homodimer generated after removal of the signal peptide. The reduced monomer comprises 354 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 40.0 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the monomer migrates as an approximately 60-65 kDa protein in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Ser 19 |
| SDS-PAGE | 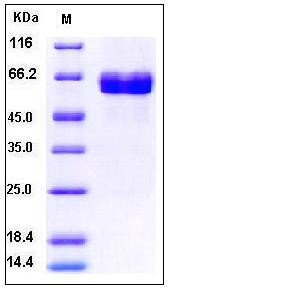 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the N-terminal segment (Met 1-Thr 134) from the extracellular domain of human ACVR2B (NP_001097.2) was expressed with the fused human IgG1 Fc region at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | 1. Measured by its ability to neutralize Activin-mediated inhibition on MPC11 cell proliferation. The ED50 for this effect is typically 0.02-0.1 µg/mL in the presence of 10 ng/mL recombinant Activin A. 2. Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. 3. Immobilized human ACVR2B (P10229-H02H) at 10 μg/mL (100 μl/well) can bind biotinylated human INHBA-His (P10429-H08H), The EC50 of biotinylated human INHBA-His (P10429-H08H) is 0.112 μg/mL. 4. Immobilized human ACVR2B (P10229-H02H) at 10 μg/mL (100 μl/well) can bind biotinylated mouse INHBA-His (PCat:50659-M08H), The EC50 of biotinylated mouse INHBA-His (PCat:50659-M08H) is 0.161 μg/mL. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Cytoskeleton / ECM |Cytoskeletal Proteins |Microfilaments |Actin etc | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | ACVR2A and ACVR2B are two activin type II receptors. ACVR2B is integral to the activin and myostatin signaling pathway. Ligands such as activin and myostatin bind to ACVR2A and ACVR2B. Myostatin, a negative regulator of skeletal muscle growth, is regarded as a potential therapeutic target and binds to ACVR2B effectively, and to a lesser extent, to ACVR2A. The structure of human ACVR2B kinase domain in complex with adenine establishes the conserved bilobal architecture consistent with all other catalytic kinase domains. Haplotype structure at the ACVR2B and follistatin loci may contribute to interindividual variation in skeletal muscle mass and strength. Defects in ACVR2B are a cause of left-right axis malformations. |
| Reference |
|
