Human ADGRE5 / CD97 Protein (His Tag)
CD97,TM7LN1
- 100ug (NPP3725) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11280-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CD97,TM7LN1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CD97 consists of 389 amino acids and predictes a molecular mass of 42.6 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rh CD97 is approximately 60-70 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Gln 21 |
| SDS-PAGE | 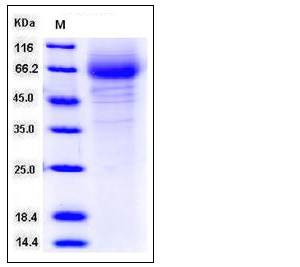 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the first 398 amino acids (Met 1-Gln 398) of human CD97 isoform 2 (NP_001775.2) extracellular domain was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA . Immobilized recombinant human CD97 at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind recombinant human CD55 at a linear range of 0.46-30 μg/ml. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Innate Immunity |Monocytes/Macrophages |Macrophage Markers |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | The cluster of differentiation (CD) system is commonly used as cell markers in immunophynotyping. Different kinds of cells in the immune system can be identified through the surface CD molecules which associating with the immune function of the cell. There are more than 320 CD unique clusters and subclusters have been identified. Some of the CD molecules serve as receptors or ligands important to the cell through initiating a signal cascade which then alter the behavior of the cell. Some CD proteins do not take part in cell signal process but have other functions such as cell adhesion. The CD97 is a receptor predominantly expressed in leukocytes and belongs to a new group of seven-span transmembrane molecules, which is also designed EGF-TM7 family. The family members are characterized by an extended extracellular region with several N-terminal epidermal growth factor-like domains two of which contain a calcium binding site. Muture CD 97 has two noncovalently associated subunits and is composed of a large extracellular protein (CD97 alpha) and a seven-membrane spanning protein (CD97 beta). CD97 is considered as a defining feature of G protein-coupled receptors. The effects that lymphocytes and erythrocytes adere to CD97-transfected COS cells suggest that CD97 has the ability to bind cellular ligands. CD97 alpha has three alternatively spliced isforms that are related to the calium binding EGF-like repeats in the microfibril protein fibrillin. Leukocytes strongly positive for CD97 are concentrated at sites of inflammation relative to CD97 expression in normal lymphoid tissues. |
| Reference |
