Human ADK Protein (His & GST Tag)
AK
- 100ug (NPP3562) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P13149-H20B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | AK |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human ADK/GST chimera consists of 582 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 68 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 60 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 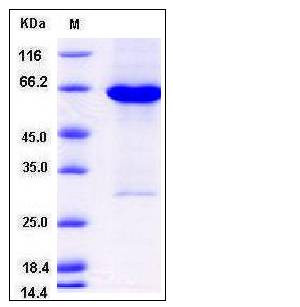 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human ADK isoform short (AAH03568.1) (Met 1-His 345) was fused with the N-terminal polyhistidine-tagged GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Kinase activity untested |
| Research Area | Cancer |Cancer Metabolism |Metabolic signaling |Integration of energy metabolism |
| Formulation | Supplied as sterile 50mM Tris, 100mM NaCl, pH 8.0, 10% gly, 0.3mM DTT 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Adenosine kinase(ADK) belongs to the family of transferases. Adenosine kinase (ADK) is the key enzyme in adenosine metabolism and catalyzes ATP and adenosine into two products: ADP and AMP. Two isoforms of the enzyme adenosine kinase (ADK), which differ at their N-terminal ends, are found in mammalian cells. It has been shown that the two ADK isoforms differ only in their first exons and the promoter regions; hence they arise via differential splicing of their first exons with the other exons common to both isoforms. In adult brain, ADK is primarily present in astrocytes. Several lines of experimental evidence support a critical role of ADK in different types of brain injury associated with astrogliosis, which is also a prominent morphologic feature of temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE). It has been suggested that dysregulation of ADK in astrocytes is a common pathologic hallmark of TLE. Moreover, in vitro data suggest the existence of an additional layer of modulatory crosstalk between the astrocyte-based adenosine cycle and inflammation. ADK also contributes to CK homeostasis in vivo. |
| Reference |
