Human ADM / Adrenomedullin Protein (Fc Tag)
AM,PAMP
- 100ug (NPP3563) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11646-H01H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | AM,PAMP |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human ADM/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 340 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 38 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 39 in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Glu |
| SDS-PAGE | 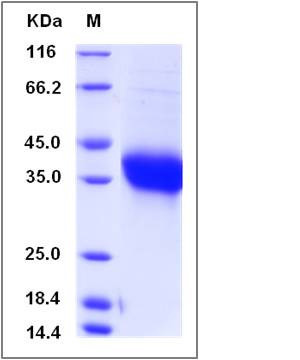 |
| Purity | > 93 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human ADM (P35318) (Tyr95-Tyr146) was expressed, with the fused Fc region of human IgG1 at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Invasion microenvironment |Angiogenesis |Growth Factor & Receptor |Hormones |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Adrenomedullin consists of 52 amino acids and is a member of the adrenomedullin family. It s a a hypotensive peptide and has 1 intramolecular disulfide bond. It seems that adrenomedullin has a slight homology with the calcitonin gene-related peptide. Adrenomedullin has a highly expression in pheochromocytoma and adrenal medulla. It also can be detected in lung, ventricle and kidney tissues. Adrenomedullin and PAMP are potent hypotensive and vasodilatator agents. Numerous actions have been reported most related to the physiologic control of fluid and electrolyte homeostasis. In the kidney, adrenomedullin is diuretic and natriuretic, and both adrenomedullin and PAMP inhibit aldosterone secretion by direct adrenal actions. In pituitary gland, both peptides at physiologically relevant doses inhibit basal ACTH secretion. Both peptides appear to act in brain and pituitary gland to facilitate the loss of plasma volume, actions which complement their hypotensive effects in blood vessels. It is believed that adrenomedullin functions through combinations of the calcitonin receptor like receptor and receptor activity-modifying proteins complexes, as well as CGRP receptors. |
| Reference |
