Human ADSL / Adenylosuccinate Lyase Protein (His Tag)
AMPS,ASASE,ASL
- 100ug (NPP1872) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11287-H07E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | AMPS,ASASE,ASL |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human ADSL comprises 500 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 57 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 53 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 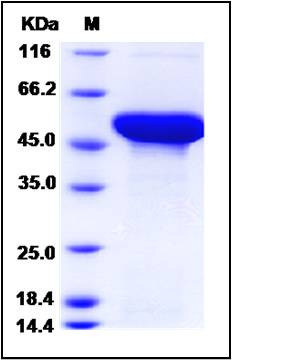 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human ADSL (P30566-1) (Met 1-Leu 484) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Metabolism |Types of disease |Metabolism in Cancer |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, 10% glycerol, pH 7.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Adenylosuccinate lyase, also known as adenylosuccinase, ADSL or ASL, is an enzyme implicated in the reaction of adenylosuccinat converting to AMP and fumarate as part of the purine nucleotide cycle. The two substates of adenylosuccinate lyase (ADSL) are dephosphorylated derivatives of SAICA ribotide (SAICAR) and adenylosuccinate (S-AMP), which catalyzes an important reaction in the de novo pathway of purine biosynthesis. ADSL catalyzes two distinct reactions in the synthesis of purine nucleotides, both of which involve the _-elimination of fumarate to produce either aminoimidazole carboxamide ribotide from SAICAR or AMP from S-AMP. The Adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency is a rare autosomal recessive metabolic disorder characterized by the present of SAICA riboside and succinyladenosine (S-Ado). ADSL defect in different patients is often caused by different mutations to the enzyme. |
| Reference |
