Human AK4 / Adenylate Kinase 4 / AK3L1 Protein (His & GST Tag)
AK3,AK3L1,AK3L2,AK4
- 100ug (NPP3568) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P12406-H20B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | AK3,AK3L1,AK3L2,AK4 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human AK4/GST chimera consists of 460 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 53 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 46 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 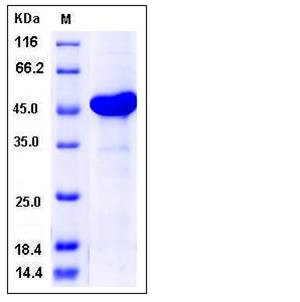 |
| Purity | > 94 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human AK4 (P27144-1) (Ala 2-Tyr 223) was fused with the N-terminal polyhistidine-tagged GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Kinase activity untested |
| Research Area | |
| Formulation | Supplied as sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, pH 8.0 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Adenylate kinase isoenzyme 4, mitochondrial, also known as ATP-AMP transphosphorylase, Adenylate kinase 3-like, AK4 and AK3L1, is a member the adenylate kinase family. AK4 / AK3L1 is localized to the mitochondrial matrix. Adenylate kinases regulate the adenine and guanine nucleotide compositions within a cell by catalyzing the reversible transfer of phosphate group among these nucleotides. Five isozymes of adenylate kinase have been identified in vertebrates. Expression of these isozymes is tissue-specific and developmentally regulated. AK4 / AK3L1 catalyzes the reversible transfer of the terminal phosphate group between ATP and AMP. It may also be active with GTP. Adenylate kinase 4 ( AK4 / AK3L1 ) is a unique member with no enzymatic activity in the adenylate kinase (AK) family although it shares high sequence homology with other AKs. It remains unclear what physiological function AK4 might play or why it is enzymatically inactive. AK4 / AK3L1 retains the capability of binding nucleotides. It has a glutamine residue instead of a key arginine residue in the active site well conserved in other AKs. The enzymatically inactive AK4 is a stress responsive protein critical to cell survival and proliferation. AK4 / AK3L1 is likely that the interaction with the mitochondrial inner membrane protein ANT is important for AK4 to exert the protective benefits to cells under stress. AK4 / AK3L1 also acts on the specific mechanism of energy metabolism rather than control of the homeostasis of the ADP pool ubiquitously. |
| Reference |
