Human ALDH7A1 / ATQ1 Protein (His Tag)
ATQ1,EPD,PDE
- 100ug (NPP1886) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11614-H07E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | ATQ1,EPD,PDE |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human ALDH7A1 consisting of 517 amino acids and migrates as an approximately 56 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions as predicted. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 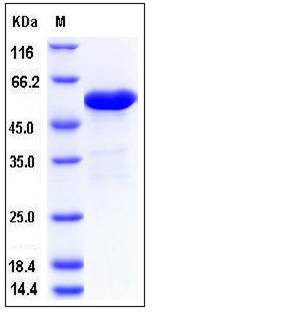 |
| Purity | > 93 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human ALDH7A1 isoform 2 (P49419-2) (Ser 2-Gln 511) was expressed, with a polyhistide tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Metabolism |Pathways and Processes |Metabolic signaling pathways |Alcohol metabolism | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, 20% glycerol, pH 8.0 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | ALDH7A1 (Aldehyde dehydrogenase 7 family, member A1) is a member of subfamily 7 in the aldehyde dehydrogenase family. These enzymes are thought to play a major role in the detoxification of aldehydes generated by alcohol metabolism and lipid peroxidation. Mammalian ALDH7A1 is homologous to plant ALDH7B1 which protects against various forms of stress such as increased salinity, dehydration and treatment with oxidants or pesticides. In mammals, ALDH7A1 is known to play a primary role during lysine catabolism through the NAD+-dependent oxidative conversion of aminoadipate semialdehyde (AASA) to its corresponding carboxylic acid, α-aminoadipic acid. Deleterious mutations in human ALDH7A1 are responsible for pyridoxine-dependent and folinic acid-responsive seizures. ALDH7A1 is a novel aldehyde dehydrogenase expressed in multiple subcellular compartments that protects against hyperosmotic stress by generating osmolytes and metabolizing toxic aldehydes. |
| Reference |
