Human ALK-1 / ACVRL1 Protein (His Tag)
ACVRLK1,ALK-1,ALK1,HHT,HHT2,ORW2,SKR3,TSR-I
- 100ug (NPP1055) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10066-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | ACVRLK1,ALK-1,ALK1,HHT,HHT2,ORW2,SKR3,TSR-I |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human ALK1 comprises 108 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 12.3 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, rhALK1 migrates as an approximately 27 kDa protein in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Asp 22 |
| SDS-PAGE | 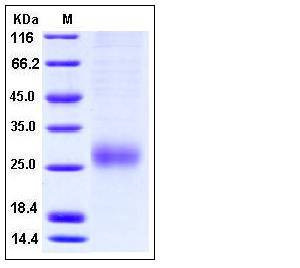 |
| Purity | > 92 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the the extracellular domain of human ALK1 (NP_000011.2) (Met 1-Gln 118) was fused with a polyhistide tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to inhibit BMP9 induced alkaline phosphatase production by MC3T3E1 mouse chondrogenic cells. David, L. et al. (2007) Blood 109:1953. The ED50 for this effect is typically 50-200 ng/mL in the presence of 2 ng/mL of recombiant human BMP9. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Invasion microenvironment |Angiogenesis |Adhesion Molecules in Angiogenesis |Extracellular Matrix |Structures | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Activin A receptor, type II-like 1 (ACVRL1), also known as ALK-1 (activin receptor-like kinase 1), is an endothelial-specific type I receptor of the TGF-beta (transforming growth factor beta) receptor family of ligands. On ligand binding, a heteromeric receptor complex forms consisting of two type II and two type I transmembrane serine/threonine kinases. ACVRL1 protein is expressed in certain blood vessels of kidney, spleen, heart and intestine, serving as an important role during vascular development. Mutations in ACVRL1 gene are associated with hemorrhagic telangiectasia type 2, also known as Rendu-Osler-Weber syndrome 2 and vascular disease. |
| Reference |
