Human APOL1 / apolipoprotein L1 Protein (His Tag)
APO-L,APOL,APOL-I,APOL1,FSGS4
- 100ug (NPP1905) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P13910-H08B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | APO-L,APOL,APOL-I,APOL1,FSGS4 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human APOL1 consists of 381 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 42.5 KDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 44 KDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Glu 28 |
| SDS-PAGE | 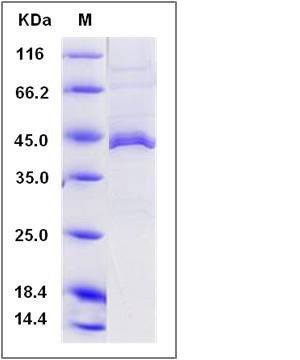 |
| Purity | > 91 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human APOL1 (Met 1-Leu398) (Q2KHQ6) was expressed, with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Metabolism |Pathways and Processes |Metabolic signaling pathways |Lipid and lipoprotein metabolism |Lipoprotein metabolism | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, pH 7.4, 10% gly, 3mM DTT 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | APOL1, also known as apolipoprotein L1, is a minor apoprotein component of HDL (High-density lipoprotein) or 'good cholesterol' which is synthesized in the liver and also in many other tissues, including pancreas, kidney, and brain. APOL1 belongs to the apolipoprotein L family. It may play a role in lipid exchange and transport throughout the body. It may also participate in reverse cholesterol transport from peripheral cells to the liver. Defects in APOL1 are the cause of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis type 4 (FSGS4). It is a renal pathology defined by the presence of segmental sclerosis in glomeruli and resulting in proteinuria, reduced glomerular filtration rate and edema. Renal insufficiency often progresses to end-stage renal disease, a highly morbid state requiring either dialysis therapy or kidney transplantation. |
| Reference |
