Human APOM Protein (Fc Tag)
apo-M,G3a,HSPC336,NG20
- 100ug (NPP3582) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P13495-H02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | apo-M,G3a,HSPC336,NG20 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human APOM/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimeric protein. The reduced monomer consists of 407 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 45.6 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the reduced monomer is approximately 50 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Cys 23 |
| SDS-PAGE | 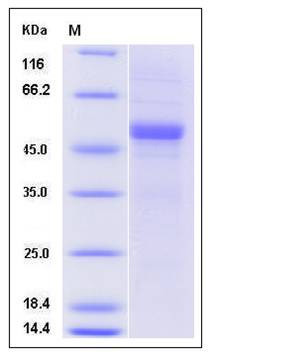 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human APOM (O95445) (Met 1-Asn 188) was fused with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Metabolism |Pathways and Processes |Metabolic signaling pathways |Lipid and lipoprotein metabolism |Lipid metabolism | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | ApoM (apolipoprotein M) is an apolipoprotein and member of the lipocalin protein family. The lipocalins share limited regions of sequence homology and a common tertiary structure architecture. They have an eight-stranded, antiparallel, symmetrical _-barrel fold, which is in essence a beta sheet which has been rolled into a cylindrical shape. Inside this barrel is located a ligand binding site. They transport small hydrophobic molecules such as steroids, bilins, retinoids, and lipids. Lipocalins have been associated with many biological processes, among them immune response, pheromone transport, biological prostaglandin synthesis, retinoid binding, and cancer cell interactions. Lipocalins are comparatively small in size, and are thus less complicated to study as opposed to large, bulky proteins. They can also bind to various ligands for different biological purposes. ApoM is associated with high density lipoproteins and to a lesser extent with low density lipoproteins and triglyceride-rich lipoproteins. ApoM is involved in lipid transport and can bind sphingosine-1-phosphate, myristic acid, palmitic acid and stearic acid, retinol, all-trans-retinoic acid and 9-cis-retinoic acid. |
| Reference |
