Human ATP1B1 Protein (His Tag)
ATP1B
- 100ug (NPP1917) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P14255-H07H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | ATP1B |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human ATP1B1 comprises 261 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 30.4 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 40-47 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | His |
| SDS-PAGE | 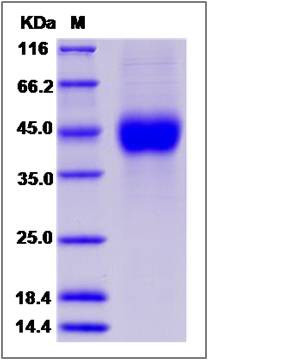 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human ATP1B1 (P05026-1) (Glu63-Ser303) was expressed with an N-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Metabolism |Plasma Membrane |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | ATP1B1 belongs to the family of Na+/K+ and H+/K+-ATPases beta chain proteins, and to the subfamily of Na+/K+ -ATPases. ATP1B1 is a subunit of Na+/K+-ATPase. Na+/K+-ATPase is an integral membrane protein responsible for establishing and maintaining the electrochemical gradients of Na and K ions across the plasma membrane. Na+/K+-ATPase is composed of two subunits, a large catalytic subunit (alpha) and a smaller glycoprotein subunit (beta). ATP1B1 regulates, through assembly of alpha/beta heterodimers, the number of sodium pumps transported to the plasma membrane. ATP1B1 is the non-catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of Na+ and K+ ions across the plasma membrane. |
| Reference |
