Human Alkaline Phosphatase / ALPL Protein (His Tag)
AP-TNAP,APTNAP,HOPS,TNAP,TNSALP
- 100ug (NPP3576) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10440-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | AP-TNAP,APTNAP,HOPS,TNAP,TNSALP |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human ALPL consists of 496 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 55 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, rhALPL migrates as approximately 65 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Leu 18 |
| SDS-PAGE | 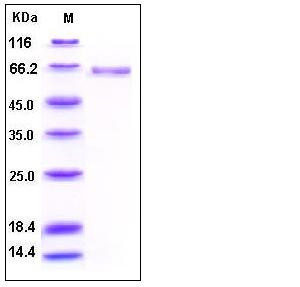 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (NP_000469.3) (Met 1-Ser 502) was expressed with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to cleave a fluorogenic substrate, 4-Methylumbelliferyl phosphate (4-MUP). The specific activity is > 50, 000 pmoles/min/μg. |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Phosphatase & Regulator |Phosphatase |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 25mM Tris, 0.15M NaCl, pH 7.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Alkaline phosphatase (ALPL) is a hydrolase enzyme responsible for removing phosphate groups from many types of molecules, including nucleotides, proteins, and alkaloids. The process of removing the phosphate group is called dephosphorylation. As the name suggests, alkaline phosphatases are most effective in an alkaline environment. It is sometimes used synonymously as basic phosphatase. Alkaline phosphatases (APs) are ubiquitous in many species, from bacteria to human. Four genes encode AP isoenzymes in humans and rodents. Three AP genes are expressed in a tissue-specific manner (i.e., placental, embryonic, and intestinal AP isoenzymes). Expression of the fourth AP gene is nonspecific to a single tissue and is especially abundant in bone, liver, and kidney. This isoenzyme is also called tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (TNAP). The enzyme tissue non-specific alkaline phosphatase (TNAP) belongs to the ectophosphatase family. TNAP is present in large amounts in bone in which it plays a role in mineralization. |
| Reference |
