Human B2M / Beta-2-microglobulin Protein (His Tag)
Beta-2 microglobulin
- 100ug (NPP3587) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11976-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | Beta-2 microglobulin |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human B2M consists of 110 amino acids and migrates as an approximately 13.5 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions as predicted. |
| predicted N | Ile 21 |
| SDS-PAGE | 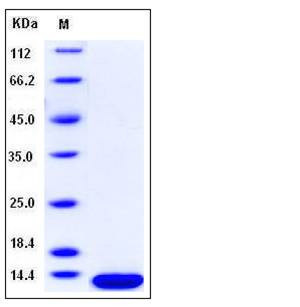 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human B2M (NP_004039.1) (Met 1-Met 119) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Oncoprotein & suppressor & biomarker |Tumor biomarker |Other in cancer biomarker |Globulin |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | B2M, also known as β2-Microglobulin or CDABP0092, is a component of MHC class I molecules found expression in all nucleated cells (excludes red blood cells). The major function of MHC class I moleculesis is to display fragments of proteins from within the cell to T-cells and cells containing foreign proteins will be attacked. B2M(β2-Microglobulin) is a low molecular weight protein. It was demonstrated that B2M(β2-Microglobulin) was localized in the membranes of nucleated cells and was found to be associated with HL-A antigens.B2M(β2- Microglobulin) is present in free form in various body fluids and as a subunit of histocompatibility antigens on cell surfaces lateral to theα3 chain. Unlikeα3, β2 has no transmembrane region. Directly above β2 lies the α1 chain, which itself is lateral to the α2. In the absence of B2M(β2 microglobulin), very limited amounts of MHC class I (classical and non-classical) molecules can be detected on the surface. In the absence of MHC class I, CD8 T cells, a subset of T cells involved in the development of acquired immunity cannot develop. Low levels of B2M(β2 microglobulin) can indicate non-progression of HIV. |
| Reference |
