Human B4GALT1 / GGTB2 Protein (His Tag)
B4GAL-T1,beta4Gal-T1,CDG2D,GGTB2,GT1,GTB
- 100ug (NPP3588) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11220-H07H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | B4GAL-T1,beta4Gal-T1,CDG2D,GGTB2,GT1,GTB |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human B4GALT1 consists of 371 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 41.5 kDa. By SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, rh B4GALT1 migrates as an approximately 45-55 kDa protein due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | His |
| SDS-PAGE | 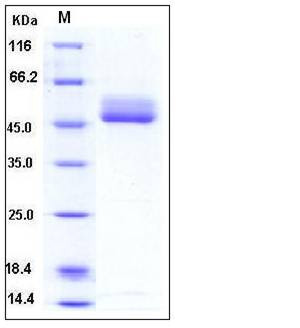 |
| Purity | > 92 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human B4GALT1 extracellular domain (NP_001488.2) (Gly 44-Ser 398) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Reproduction |Fertilization |Gamete Fusion |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Beta1,4-Galactosyltransferase-I (B4GALT1), one of seven beta1,4-galactosyltransferases, is an enzyme commonly found in the trans-Golgi complex that adds galactose to oligosaccharides. They have an N-terminal hydrophobic signal sequence that directs the protein to the Golgi apparatus and which then remains uncleaved to function as a transmembrane anchor. By sequence similarity, the beta4GalTs form four groups: beta4GalT1 and beta4GalT2, beta4GalT3 and beta4GalT4, beta4GalT5 and beta4GalT6, and beta4GalT7. B4GALT1 gene directs production of B4GALT1 protein using either of two transcription start sites. The product of the smaller transcript serves the traditional biosynthetic role in the Golgi. This form also complexes with α-lactalbumin, a mammary-specific protein, to form lactose synthase. In addition to a biosynthetic role, the protein translated from the longer transcript appears on the plasma membranes of some cells where it serves as a signalling receptor in cell-matrix interactions such as sperm-egg binding. |
| Reference |
