Human B7-H4 / B7S1 / B7x Protein (Fc Tag)
B7-H4,B7h.5,B7H4,B7S1,B7X,PRO1291,VCTN1
- 100ug (NPP3590) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10738-H02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | B7-H4,B7h.5,B7H4,B7S1,B7X,PRO1291,VCTN1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human VTCN1/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 471 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 52.3 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 66-76 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Phe 29 |
| SDS-PAGE | 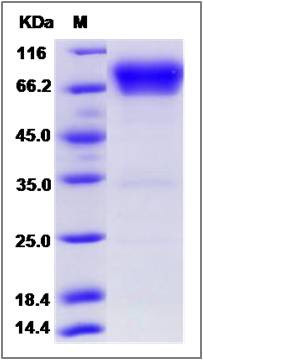 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human VTCN1 (Q7Z7D3-1) (Phe29-Ala258) was expressed, fused with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Innate Immunity |Monocytes/Macrophages |Co-stimulatory Molecules |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | V-set domain-containing T-cell activation inhibitor 1, also known as B7X, B7H4, B7S1, and VTCN1, is a single-pass type? membrane protein belonging to the B7 family of costimulatory proteins. These proteins are expressed on the surface of antigen-presenting cells and interact with ligands on T lymphocytes. They provide costimulatory signals that regulate T cell responses. A soluble form of B7H4 has also been detected. B7X / VTCN1 / B7H4 negatively regulates T-cell-mediated immune response by inhibiting T-cell activation, proliferation, cytokine production and development of cytotoxicity. When expressed on the cell surface of tumor macrophages, B7X / VTCN1 / B7H4 plays an important role, together with regulatory T-cells(Treg), in the suppression of tumor-associated antigen-specific T-cell immunity. B7X / VTCN1 / B7H4 is also involved in promoting epithelial cell transformation. This membrane protein can be up-regulated by IL6 / interleukin-6 and IL10 / interleukin-10 and inhibited by CSF2 / GM-CSF and IL4 / interleukin-4 on antigen-presenting cells. |
| Reference |
