Human BCAM Protein (Fc Tag)
AU,CD239,LU,MSK19
- 100ug (NPP3684) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10238-H02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | AU,CD239,LU,MSK19 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human BCAM/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimeric protein. The reduced monomer consists of 754 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 83 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the rh BCAM/Fc monomer migrates as approximately 100-110 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Glu 32 |
| SDS-PAGE | 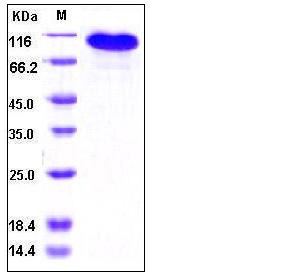 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of human BCAM (NP_005572.2) (Met 1-Ala 547) was fused with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Cytoskeleton / ECM |Cell Adhesion |Lectin |C-tyep lectin | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | The Lutheran (Lu) blood group and basal cell adhesion molecule (BCAM) antigens are both carried by 2 glycoprotein isoforms of the immunoglobulin superfamily representing receptors for the laminin alpha(5) chain. It is a transmembrane receptor with five immunoglobulin-like domains in its extracellular region, and is therefore classified as a member of the immunoglobulin (Ig) gene family. In addition to red blood cells, Lu/BCAM proteins are expressed in endothelial cells of vascular capillaries and in epithelial cells of several tissues. BCAM/LU has a wide tissue distribution with a predominant expression in the basal layer of the epithelium and the endothelium of blood vessel walls. As designated as CD239 recently, BCAM and LU share a significant sequence similarity with the CD146 (MUC18) and CD166, and themselves are adhesion molecules that bind laminin with high affinity. Laminins are found in all basement membranes and are involved in cell differentiation, adhesion, migration, and proliferation. BCAM is upregulated following malignant transformation of some cell types in vivo and in vitro, thus being a candidate molecule involved in tumor progression. In addition, BCAM interacts with integrin in sickle red cells, and thus may potentially play a role in vaso-occlusive episodes. |
| Reference |
