Human BCHE / Butyrylcholinesterase Protein (His Tag)
CHE1,CHE2,E1
- 100ug (NPP3597) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P12010-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CHE1,CHE2,E1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human BCHE consists of 585 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 66.5 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rh BCHE is approximately 85-95 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Glu 29 |
| SDS-PAGE | 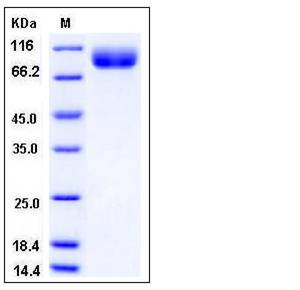 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human BCHE (NP_000046.1) (Met 1-Leu 602) was expressed, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to cleave Butyrylthiocholine . The specific activity is >50,000 pmoles/min/μg . |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Metabolism |Types of disease |Metabolism in Neurodegenerative disease |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Butyrylcholinesterase (BCHE), also known as cholinesterase or BuChE, is an enzyme defined as "pseudo" or "non-neuronal" cholinesterase. Butyrylcholinesterase (BCHE) is widely distributed in the nervous system as well as blood plasma. It is constitutively similar to the neuronal acetylcholinesterase, and is a non-specific cholinesterase which hydrolyses many different choline esters. Butyrylcholinesterase (BCHE) is a glycoprotein of 4 identical subunits, that were arranged as a dimer of dimers with each dimer composed of two identical subunits joined by interchain disulfide bonds. Butyrylcholinesterase (BCHE) behaves principally similar to the true enzyme and thus can play a similar role in nerve conduction, although it participates probably only in relatively slow conductive processes and could be involved in other nervous system functions and in neurodegenerative diseases. It can hydrolyze toxic esters such as cocaine or scavenge organophosphorus pesticides and nerve agents. Purified human serum cholinesterase combines in its active surface an anionic and an esteratic site, similar to true cholinesterase. It has been demonstrated that butyrylcholinesterase (BCHE) may have a greater role in cholinergic transmission than previously surmised, making BChE inhibition an important therapeutic goal in Alzheimer's disease. |
| Reference |
