Human BID Protein
FP497
- 100ug (NPP3606) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10468-HNCE |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | FP497 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human BID consists of 197 amino acids and migrates as an approximately 22 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions as predicted. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 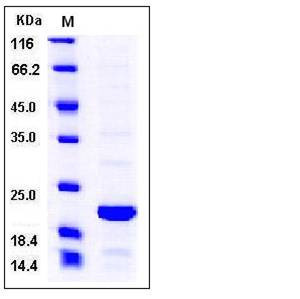 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human BID isoform 1 (P55957-1) (Met 1-Asp 195) was expressed and purified, with additional two amino acids (Gly & Pro) at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | 1. Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. 2. Immobilized human BID at 10 μg/mL (100 μl/well) can bind biotinylated human BCL2L1, The EC50 of biotinylated human BCL2L1 is 7.1 ng/mL. 3. Immobilized human BID at 10 μg/mL (100 μl/well) can bind biotinylated mouse BCL2L1, The EC50 of biotinylated mouse BCL2L1 is 5.6 ng/mL. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Metabolism |Pathways and Processes |Metabolism processes |Apoptosis | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 40mM Tris, 150mM NaCl, pH 8.0 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | The BH3 interacting domain death agonist (BID) is a pro-apoptotic member of the Bcl-2 protein family, which contains only the BH3 domain, and is required for its interaction with the Bcl-2 family proteins and for its pro-death activity. BID is important to cell death mediated by these proteases and thus is the sentinel to protease-mediated death signals. Recent studies further indicate that Bid may be more than just a killer molecule, it could be also involved in the maintenance of genomic stability by engaging at mitosis checkpoint. BID is an integrating key regulator of the intrinsic death pathway that amplifies caspase-dependent and caspase-independent execution of neuronal apoptosis. Therefore pharmacological inhibition of BID provides a promising therapeutic strategy in neurological diseases where programmed cell death is prominent. BID is activated by Caspase 8 in response to Fas/TNF-R1 death receptor activation. Activated BID is translocated to mitochondria and induces cytochrome c release, which in turn activates downstream caspases. BID action has been proposed to involve the mitochondrial re-location of its truncated form, tBid, to facilitate the release of apoptogenic proteins like cytochrome c. |
| Reference |
