Human BLMH / BLM hydrolase Protein (His Tag)
BH,BMH
- 100ug (NPP1929) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11333-H07E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | BH,BMH |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human BLMH consisting of 461 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 53.4 kDa as estimated in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 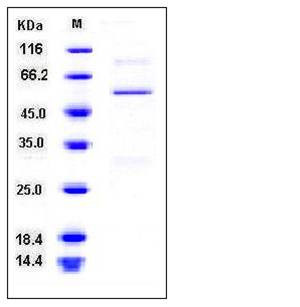 |
| Purity | > 88 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human BLMH (NP_000377.1) (Ser 2-Glu 455) was expressed, with a polyhistide tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to hydrolyze Met-AMC . The specific activity is >500 pmoles/min/μg. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Cancer Metabolism |Metabolic signaling |Metabolism of carbohydrate |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | The papain superfamily member bleomycin hydrolase (BLMH) is a cytoplasmic cysteine peptidase that is highly conserved through evolution. The only known activity of the enzyme is metabolic inactivation of the glycopeptide bleomycin (BLM), an essential component of combination chemotherapy regimens for cancer. The papain superfamily member bleomycin hydrolase (BLMH) is a neutral cysteine protease with structural similarity to a 20S proteasome. Bleomycin (BLM), a clinically used glycopeptide anticancer agent. BLMH is an essential protectant against BLM-induced death and has an important role in neonatal survival and in maintaining epidermal integrity. Sequencing revealed several putative sites phosphorylated by different types of protein kinases, but no signal sequence, transmembrane domain, N-linked glycosylation site or DNA-binding motif. |
| Reference |
