Human BLNK / Ly-57 / SLP-65 Protein (His Tag)
AGM4,BASH,bca,BLNK-S,LY57,SLP-65,SLP65
- 100ug (NPP3608) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P12706-H07H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | AGM4,BASH,bca,BLNK-S,LY57,SLP-65,SLP65 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human BLNK consists of 476 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 53 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rh BLNK is approximately 95-100 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | His |
| SDS-PAGE | 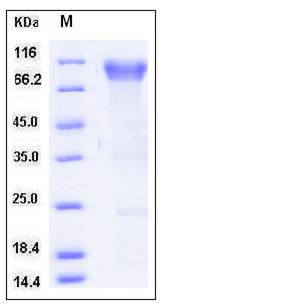 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human BLNK isoform 1 (AAH18906.1) (Met 1-Ser 456) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to bind human BTK in a functional ELISA. |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Metabolism |Vitamins / Minerals |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | B-cell linker protein, also known as B-cell adapter containing a SH2 domain protein, B-cell adapter containing a Src homology 2 domain protein, Cytoplasmic adapter protein, Src homology 2 domain-containing leukocyte protein of 65 kDa, SLP-65 and BLNK, is a cytoplasm and cell membrane protein which contains one SH2 domain. BLNK is expressed in B-cell lineage and fibroblast cell lines. Highest levels of expression is in the spleen, with lower levels in the liver, kidney, pancreas, small intestines and colon. BLNK functions as a central linker protein that bridges kinases associated with the B-cell receptor (BCR) with a multitude of signaling pathways, regulating biological outcomes of B-cell function and development. BLNK plays a role in the activation of ERK / EPHB2, MAP kinase p38 and JNK. BLNK modulates AP1 activation. It is important for the activation of NF-kappa-B and NFAT. BLNK plays an important role in BCR-mediated PLCG1 and PLCG2 activation and Ca2+ mobilization and is required for trafficking of the BCR to late endosomes. BLNK may be required for the RAC1-JNK pathway. It plays a critical role in orchestrating the pro-B cell to pre-B cell transition. BLNK also plays an important role in BCR-induced B-cell apoptosis. Defects in BLNK are the cause of agammaglobulinemia type 4 (AGM4) which is a primary immunodeficiency characterized by profoundly low or absent serum antibodies and low or absent circulating B cells due to an early block of B-cell development. |
| Reference |
