Human BLyS / TNFSF13B / BAFF Protein
BAFF,BLYS,CD257,DTL,TALL-1,TALL1,THANK,TNFSF20,ZTNF4
- 100ug (NPP3611) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10056-HNCH |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | BAFF,BLYS,CD257,DTL,TALL-1,TALL1,THANK,TNFSF20,ZTNF4 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human BAFF consists of 152 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 17 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, rhBAFF is migrates as an approximately 19 kDa band. |
| predicted N | Ala 134 |
| SDS-PAGE | 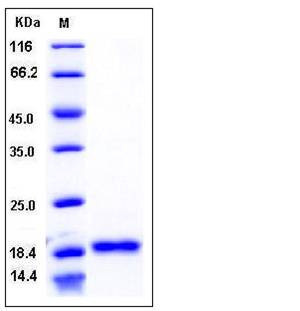 |
| Purity | > 96 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the soluble form of human BAFF (Q9Y275-1) (Ala 134-Leu 285) was expressed and purified. |
| Bio-activity | Measured in a cell proliferation assay using anti-IgM stimulated mouse B cells. The ED50 for this effect is typically 0.4-2 ng/mL in the presence of goat anti-mouse IgM μ chain. |
| Research Area | Cardiovascular |Angiogenesis |Cytokines / Chemokines in Angiogenesis |TNF Superfamily |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | B lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS), also known as TNFSF13B, CD257 and BAFF, is single-pass type II membrane protein, which belongs to the tumor necrosis factor family. BAFF is abundantly expressed in peripheral blood Leukocytes and is specifically expressed in monocytes and macrophages. BAFF is a cytokine and serves as a ligand for receptors TNFRSF13B (TACI), TNFRSF17 (BCMA), and TNFRSF13C (BAFFR). These receptors is a prominent factor in B cell differentiation, homeostasis, and selection. BLyS levels affect survival signals and selective apoptosis of autoantibody-producing B cells. Thus, it acts as a potent B cell activator and has been shown to play an important role in the proliferation and differentiation of B cells. Overexpression of BLyS in mice can lead to clinical and serological features of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and Sjögren's syndrome (SS). BLyS as an attractive therapeutic target in human rheumatic diseases. The ability of BLyS to regulate both the size and repertoire of the peripheral B cell compartment raises the possibility that BLyS and antagonists thereof may form the basis of a therapeutic trichotomy. As an agonist, BLyS protein may enhance humoral immunity in congenital or acquired immunodeficiencies such as those resulting from viral infection or cancer therapy. |
| Reference |
