Human BMPR1B / ALK-6 Protein (Fc Tag)
ALK-6,ALK6,CDw293
- 100ug (NPP1086) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10460-H02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | ALK-6,ALK6,CDw293 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human ALK6/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 354 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 39.7 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 110 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Lys 14 |
| SDS-PAGE | 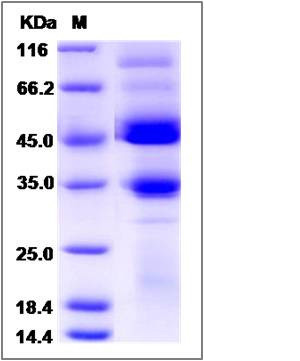 |
| Purity | (54.4+36.1) % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human ALK6 (Lys14-Arg126) was expressed with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to inhibit rhBMP4-induced alkaline phosphatase production by MC3T3-E1 mouse osteoblastic cells. The ED50 for this effect is typically 2-8 μg/mL in the presence of 50 ng/mL of recombinant human BMP4. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Invasion microenvironment |Angiogenesis |Cytokine & Receptor |Transforming Growth Factor Beta (TGF-beta) Superfamily |TGF-beta Superfamily Receptors | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | BMPR1B(bone morphogenetic protein receptor, type IB), also known as ALK6, is a a member of the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) receptor family. BMPs are involved in endochondral bone formation and embryogenesis. These proteins transduce their signals through the formation of heteromeric complexes of 2 different types of serine (threonine) kinase receptors: type I receptors of about 50-55 kD and type II receptors of about 70-80 kD. Type II receptors bind ligands in the absence of type I receptors, but they require their respective type I receptors for signaling, whereas type I receptors require their respective type II receptors for ligand binding. BMPR1B is the major transducer of signals in precartilaginous condensations as demonstrated in experiments using constitutively active BMPR1B receptors. BMPR1B is a more effective trasducer of GDF5 than BMPR1A. Unlike BMPR1A null mice, which die at an early embryonic stage, BMPR1B null mice are viable. |
| Reference |
