Human BMPRIA / ALK-3 / CD292 Protein (His Tag)
10q23del,ACVRLK3,ALK3,CD292,SKR5
- 100ug (NPP3574) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10446-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | 10q23del,ACVRLK3,ALK3,CD292,SKR5 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human ALK3 consists of 141 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 15.7 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rhALK3 is approximately 28-33 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Gln 24 |
| SDS-PAGE | 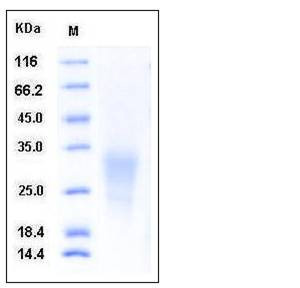 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain (Met 1-Arg 152) of human ALK3 (NP_004320.2) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to inhibit BMP4-induced alkaline phosphatase production by MC3T3E1 mouse preosteoblast cells. The ED50 for this effect is 2.5-10 μg/mL. |
| Research Area | Cardiovascular |Angiogenesis |Cytokine & Receptor |Transforming Growth Factor Beta (TGF-beta) Superfamily |TGF-beta Superfamily Receptors |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Activin receptor-Like Kinase 3 (ALK-3), also known as Bone Morphogenetic Protein Receptor, type IA (BMPR1A), is a type I receptor for bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) which belong to the transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) superfamily. The BMP receptors form a subfamily of transmembrane serine/threonine kinases including the type I receptors BMPR1A and BMPR1B and the type II receptor BMPR2. ALK-3/BMPR1A is expressed in the epithelium during branching morphogenesis. Deletion of BMPR1A in the epithelium with an Sftpc-cre transgene leads to dramatic defects in lung development. ALK-3 and ALK-6 share a high degree of homology, yet possess distinct signaling roles. The transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta type III receptor (TbetaRIII) enhanced both ALK-3 and ALK-6 signaling. TbetaRIII associated with ALK-3 primarily through their extracellular domains, whereas its interaction with ALK-6 required both the extracellular and cytoplasmic domains. ALK-3 plays an essential role in the formation of embryonic ventral abdominal wall, and abrogation of BMP signaling activity due to gene mutations in its signaling components could be one of the underlying causes of omphalocele at birth. The type IA BMP receptor, ALK-3 was specifically required at mid-gestation for normal development of the trabeculae, compact myocardium, interventricular septum, and endocardial cushion. Cardiac muscle lacking ALK-3 was specifically deficient in expressing TGFbeta2, an established paracrine mediator of cushion morphogenesis. Hence, ALK-3 is essential, beyond just the egg cylinder stage, for myocyte-dependent functions and signals in cardiac organogenesis. |
| Reference |
