Human BPI Protein (His Tag)
BPIFD1,rBPI
- 100ug (NPP3614) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P13907-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | BPIFD1,rBPI |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human BPI comprises 467 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 52.1 kDa. |
| predicted N | Val 32 |
| SDS-PAGE | 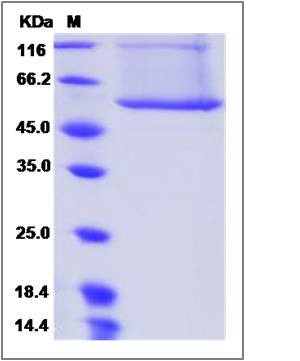 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human BPI (P17213) (Met1-Lys487) with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag was expressed. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein is a member of the BPI/LBP/Plunc superfamily and BPI/LBP family. It is a cationic protein which can be detected in the azurophilic granule and on the surface of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein also is a lipopolysaccharide binding protein. It is associated with human neutrophil granules and has bactericidal activity on gram-negative organisms. Bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein contains two domains that adopt the same structural fold, even though they have little sequence similarity. It binds to and neutralises lipopolysaccharides from the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. The cytotoxic action of bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein is limited to many species of Gram-negative bacteria; this specificity may be explained by a strong affinity of the very basic N-terminal half for the negatively charged lipopolysaccharides that are unique to the Gram-negative bacterial outer envelope. |
| Reference |
