Human C7 / Complement component 7 Protein (His Tag)
C7
- 100ug (NPP1946) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P13848-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | C7 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human C7 comprises 832 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 92.6 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 92-98 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Ser 23 |
| SDS-PAGE | 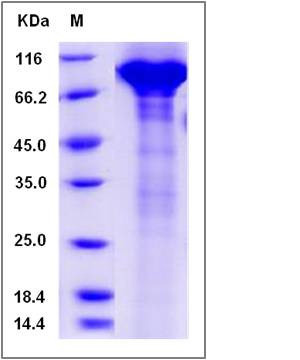 |
| Purity | > 88 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human C7 (P10643) (Met1-Gln843) with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag was expressed. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Innate Immunity |Complement System |Classical Pathway |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Complement component 7 is a component of the complement system. It belongs to the complement C6/C7/C8/C9 family. It contains 1 EGF-like domain, 1 LDL-receptor class A domain, 1 MACPF domain, 2 Sushi (CCP/SCR) domains and 2 TSP type-1 domains. Complement component 7 serves as a membrane anchor. It participates in the formation of Membrane Attack Complex (MAC). People with C7 deficiency are prone to bacterial infection. It is a constituent of MAC that plays a key role in the innate and adaptive immune response by forming pores in the plasma membrane of target cells. Defects in C7 are a cause of complement component 7 deficiency (C7D). A rare defect of the complement classical pathway associated with susceptibility to severe recurrent infections, predominantly by Neisseria gonorrhoeae or Neisseria meningitidis. |
| Reference |
