Human CA5A / CA-VA Protein (His Tag)
CA5,CA5AD,CA5D,Carbonic Anhydrase VA,CAV,CAVA,GS1-21A4.1
- 100ug (NPP1963) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10500-H08E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | CA5,CA5AD,CA5D,Carbonic Anhydrase VA,CAV,CAVA,GS1-21A4.1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CA5A consisting of 277 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 31.6 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 33 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 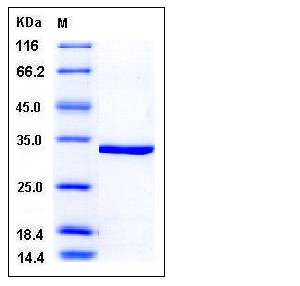 |
| Purity | > 96 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mature form of human CA5A (NP_001730.1) (Ala 40-Ser 305) was fused with an Met at N-terminus and a polyhistide tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its esterase activity. The specific activity is >500 pmoles/min/μg. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Metabolism |Types of disease |Metabolism in Cancer |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM NaAc, 50mM NaCl, 0.05% Brij 35, pH 5.0 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Carbonic anhydrase 5A, mitochondrial, also known as Carbonate dehydratase VA, Carbonic anhydrase VA, CA-VA and CA5A, is a member of the alpha-carbonic anhydrase family. Carbonic anhydrases (CAs) are a large family of zinc metalloenzymes first discovered in 1933 that catalyze the reversible hydration of carbon dioxide. CAs participate in a variety of biological processes, including respiration, calcification, acid-base balance, bone resorption, and the formation of aqueous humor, cerebrospinal fluid, saliva, and gastric acid. CA5A / CA-VA is activated by histamine, L-adrenaline, L- and D-histidine, and L- and D-phenylalanine. It is inhibited by coumarins, sulfonamide derivatives such as acetazolamide and Foscarnet (phosphonoformate trisodium salt). |
| Reference |
