Human CABP3 / CABP5 Protein (His Tag)
CABP3
- 100ug (NPP3621) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P13896-H07E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | CABP3 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CABP5 consists of 188 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 21.7 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 19 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | His |
| SDS-PAGE | 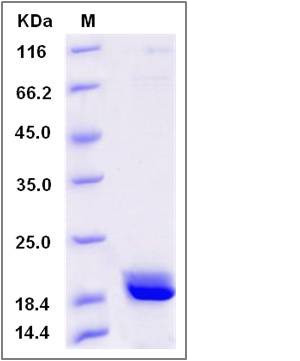 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mature form of human CABP5 (Q9NP86) (Met1-Arg173) was expressed with a polyhistide tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Signaling Pathway |Calcium Signaling |Calcium Channel |L-type | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, 0.1% Tween 20, 50mM Arg, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | CABP3, also known as CABP5, belongs to a subfamily of calcium binding proteins, which share similarity to calmodulin. Calcium binding proteins are an important component of calcium mediated cellular signal transduction. Expression of CABP3 gene is retina-specific. The mouse homolog of CABP3 has been shown to express in the inner nuclear layer of the retina, suggested its role in neuronal functioning. The specific function of CABP3 gene is unknown. Study of the transcripts and genomic structure revealed that the 5 end of this gene is complementary and reverse to that of the CABP5 gene, and the sequence beyond the overlapping region is nearly identical to that of CABP5. Thus, these two genes encode the protein products with distinct N-terminal halves but identical C-terminal halves. CABP3 inhibits calcium-dependent inactivation of L-type calcium channel and shifts voltage dependence of activation to more depolarized membrane potentials. It is also involved in the transmission of light signals. |
| Reference |
