Human CANT1 Protein (His Tag)
DBQD,SCAN-1,SCAN1,SHAPY
- 100ug (NPP1955) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P13124-H07H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | DBQD,SCAN-1,SCAN1,SHAPY |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CANT1 consists of 342 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 38 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rh CANT1 is approximately 40kDa. |
| predicted N | His |
| SDS-PAGE | 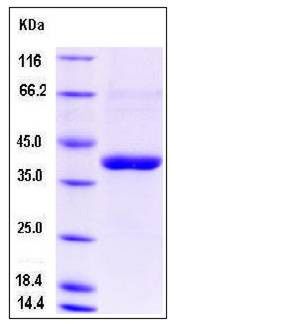 |
| Purity | > 88 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human CANT1 (Q8WVQ1-1) extracellular domain (Gly 80-Ile 401) was fused with polyhistidine tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Protein Trafficking |Golgi Proteins |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | CANT1(calcium activated nucleotidase 1) belongs to the apyrase family. Apyrase is a calcium-activated plasma membrane-bound enzyme (magnesium can also activate it) (EC 3.6.1.5) that catalyses the hydrolysis of ATP to yield AMP and inorganic phosphate. Two isoenzymes are found in commercial preparations from S. tuberosum. One with a higher ratio of substrate selectivity for ATP: ADP and another with no selectivity. It can also act on ADP and other nucleoside triphosphates and diphosphates with the general reaction being NTP -> NDP + Pi -> NMP + 2Pi. The salivary apyrases of blood-feeding arthropods are nucleotide hydrolysing enzymes are implicated in the inhibition of host platelet aggregation through the hydrolysis of extracellular adenosine diphosphate. CANT1 functions as a calcium-dependent nucleotidase with a preference for UDP. Defects in CANT1 are the cause of desbuquois dysplasia. |
| Reference |
