Human CANX / Calnexin Protein (Fc Tag)
CNX,IP90,P90
- 100ug (NPP1957) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P13929-H02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CNX,IP90,P90 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CANX/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 702 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 79.4 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 110 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | His 21 |
| SDS-PAGE | 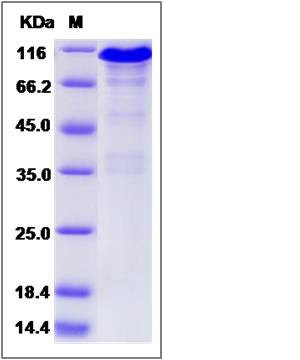 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human CANX (P27824) (Met1-Pro481) was expressed, fused with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Signaling Pathway |Calcium Signaling |Calcium Binding Protein |Calreticulin Family | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Calnexin is a calcium-binding protein that belongs to the calreticulin family. It interacts with newly synthesized glycoproteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. Calnexin seems to play a major role in the quality control apparatus of the ER by the retention of incorrectly folded proteins. It may act in assisting protein assembly and/or in the retention within the ER of unassembled protein subunits. Associated with partial T-cell antigen receptor complexes that escape the ER of immature thymocytes, it may function as a signaling complex regulating thymocyte maturation. Additionally it may play a role in receptor-mediated endocytosis at the synapse. |
| Reference |
