Human CASP7 / caspase 7 / MCH3 Protein (His Tag)
CASP-7,CMH-1,ICE-LAP3,LICE2,MCH3
- 100ug (NPP3640) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10049-H08E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | CASP-7,CMH-1,ICE-LAP3,LICE2,MCH3 |
| Molecular Weight | The full length of recombinant human CASP7 comprises 313 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 35KDa. As a result of proteolytic cleavage, the apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 20 & 11 kDa ,corresponding to the N-reminal P20 subunit and the C-teminal p11 subunit respectively in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Ala 24 & Ala 207 |
| SDS-PAGE | 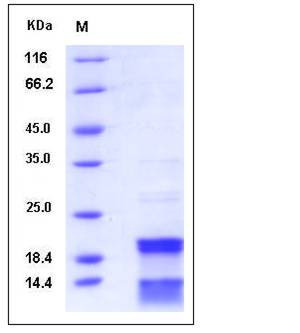 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human CASP7 (P55210-1) (Met 1-Gln 303) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Cellular Senescence and Pathways in Aging |Apoptosis |Caspase |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM HEPES, 100mM NaCl, 1mM EDTA, 0.10% Sucrose, 0.1% chaps, pH 7.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Caspase 7, also known as caspase-7 and MCH3, belongs to the cysteine-aspartic acid protease (caspase) family. Caspases play a role in the signal transduction pathways of apoptosis, necrosis and inflammation. There are two major classes of caspases: initiators and effectors. The initiator isoforms (caspases-1,-4,-5,-8,-9,-10,-11,-12) are activated by, and interact with, upstream adaptor molecules through protein-protein interaction domains known as CARD and DED. Effector caspases (-3,-6,-7) are responsible for cleaving downstream substrates and are sometimes referred to as the executioner caspases. Caspase 7 exists in lung, skeletal muscle, liver, kidney, spleen and heart, and moderately in testis. Caspase 7 cannot be detected in the brain. Caspase 7 functions in the activation cascade of caspases responsible for apoptosis execution. It cleaves and activates sterol regulatory element binding proteins (SREBPs). It proteolytically cleaves poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) at a '216-Asp- -Gly-217' bond. Overexpression promotes programmed cell death. |
| Reference |
